Anatomical aspects of the nerves of the leg and foot of the giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758)
|
|
|
- Guilherme Bergler Mangueira
- 6 Há anos
- Visualizações:
Transcrição
1 Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p , 2014 Anatomical aspects of the nerves of the leg and foot of the giant anteater (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758) [Aspectos anatômicos dos nervos da perna e pé do tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758)] V.S. Cruz 1, J.C. Cardoso 1, L.B.M. Araújo 2, P.R. Souza 1, M.S.B. Silva 1, E.G. Araújo 2 1 Universidade Federal de Goiás Instituto de Ciências Biológicas Goiânia, GO 2 Universidade Federal de Goiás Escola de Veterinária e Zootecnia Goiânia, GO ABSTRACT Although distal stifle joint nerve distribution has been well established in domestic animals, this approach is scarcely reported in wild animals. Therefore, the aim of this study was to describe the nerves of the leg and foot of Myrmecophaga tridactyla with emphasis on their ramification, distribution, topography and territory of innervation. For this purpose, six adult cadavers fixed and preserved in 10% formalin solution were used. The nerves of the leg and foot of the M. tridactyla were the saphenous nerve (femoral nerve branch), fibular and tibial nerves and lateral sural cutaneous nerve (branches of the sciatic nerve) and caudal sural cutaneous nerve (tibial nerve branch). The saphenous nerve branches to the skin, the craniomedial surface of the leg, the medial surface of the tarsal and metatarsal regions and the dorsomedial surface of the digits I and II (100% of cases), III (50% of cases) and IV (25% of cases). The lateral sural cutaneous nerve innervates the skin of the craniolateral region of the knee and leg. The fibular nerve innervates the flexor and extensor muscles of the tarsal region of the digits and skin of the craniolateral surface of the leg and dorsolateral surface of the foot. The tibial nerve innervates the extensor muscles of the tarsal joint and flexor, adductor and abductor muscles of the digits and the skin of the plantar surface. The caudal sural cutaneous nerve innervates the skin of the caudal surface of the leg. The nerves responsible for the leg and foot innervation were the same as reported in domestic and wild animals, but with some differences, such as the more distal division of the common fibular nerve, the absence of dorsal metatarsal branches of the deep fibular nerve and a greater involvement of the saphenous nerve in the digital innervation with branches to the digits III and IV, in addition to digits I and II. Keywords: pelvic limb, peripheral nervous system, enarthra RESUMO Apesar de bem estabelecida nos animais domésticos, a abordagem da distribuição nervosa distal do joelho é rara em animais selvagens. Portanto, o objetivo deste estudo foi descrever os nervos da perna e pé do Myrmecophaga tridactyla, com ênfase na sua ramificação, distribuição, topografia e território de inervação. Para tanto, foram utilizados seis cadáveres adultos, fixados e conservados em solução de formalina a 10%. A dissecação envolveu desde a formação dos nervos femoral e isquiático pelos ramos ventrais dos nervos espinhais lombares e sacrais até sua distribuição nos territórios propostos. Os nervos responsáveis pela inervação da perna e pé do M. tridactyla foram o N. safeno (ramo do N. femoral), os nervos fibular comum e tibial e o N. cutâneo lateral da sura (derivados do N. isquiático) e o N. cutâneo caudal da sura (ramo do N. tibial). O nervo safeno emite ramos cutâneos para a superfície craniomedial da perna, medial do tarso e metatarso e dorsomedial dos dedos I e II (100% dos casos), III (50% dos casos) e IV (25% dos casos). O nervo cutâneo lateral da sura inerva a região cutânea craniolateral do joelho e perna. O nervo fibular inerva os músculos flexores do tarso e extensores dos dedos e a região cutânea craniolateral da perna e dorsolateral do pé. O nervo tibial inerva os músculos Recebido em 6 de fevereiro de 2013 Aceito em 16 de dezembro de souzacruzviviane@gmail.com
2 Cruz et al. extensores do tarso e flexores, adutores e abdutores dos dedos e região cutânea plantar. O nervo cutâneo caudal da sura inerva a pele da face caudal da perna. Pode-se concluir que os nervos responsáveis pela inervação da perna e pé foram os mesmos relatados em animais domésticos e selvagens, porém com algumas diferenças, como a divisão mais distal do nervo fibular comum, ausência de ramos metatarsianos dorsais do N. fibular profundo e uma maior participação do nervo safeno na inervação digital, contribuindo com ramos inclusive para os dedos III e IV, além dos dedos I e II. Palavras-chave: membro pélvico, sistema nervoso periférico, enarthra INTRODUCTION The Myrmecophaga tridactyla is the largest mammal in the enarthra Superorder, which has recently been subdivided into the Cingulata (represented by the armadillo) and Pilosa (represented by the anteater and the sloth) orders (Vizcaíno and Loughry, 2008). The closest relatives of the same family are the Tamandua tetradactyla (lesser anteater) and the Cyclopes didactylus (silky anteater), both arboreal and smaller (Shaw et al., 1987). They inhabit the fields and savannas of the south of Belize and Guatemala up to the north of Argentina including the entire Brazilian territory (Mourão and Medri, 2007). They have laterally flattened bodies, fairly short limbs and plantigrade locomotion. The hands have long nails, which bend inwards whilst in motion (Shaw et al., 1987). The number of anteaters that have been run over has increased due to the growing number of roads running through its habitat and their necessity to move around searching for food (Braga, 2009). Additionally, the giant anteater is the large mammal most affected by bushfires (Silveira et al., 1999). For these and other reasons, this species is described as almost threatened by extinction (NT) in the International Union for Conservation of the Nature and Resources (IUCN, 2012) list, and vulnerable at a national level (Barreto, 2007). The femoral, saphenous, sciatic, common fibular, tibial and lateral cutaneous and caudal cutaneous sural nerves are responsible for the sensitive and motor innervation of the leg and foot of domestic (Getty, 1986; Schaller, 1999; Dyce et al., 2010) and wild animals (Aydin, 2009; Castro et al., 2009). Injuries to these nerves cause a variety of deficiencies, such as loss of sensitivity, muscular movement or both, in a restricted area supplied by the nerve or nerves involved (Lorenz and Kornegay, 2006). There is lack of data related to distal innervation of the locomotive limbs in wild animals and to date there are no records of studies of this nature in the pelvic limbs of any species in the enarthra superorder. Thus, this study presents unpublished and important information for many areas, especially in comparative anatomy, clinical practice, anaesthesiology and surgery of wild animals. Therefore, the aim of this study was to present a description of the nerves of the leg and foot of the M. tridactyla, with emphasis on its ramification, distribution, topography and territory of innervation. MATERIAL AND METHODS Twelve pelvic limbs of six adult giant anteaters (three females, two males and one undefined due to removal of genital organs in a necropsy procedure) were examined in this study. The cadavers were provided by IBAMA - Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources) (license 99/2011) and the experimental protocol has been approved by the Ethics Committee for Animal Use of the Federal University of Goiás - Brazil (Process CEUA- UFG no. 015/11). Preparation, storage and dissection of the specimens were held in the Laboratory of Animal Anatomy at the Institute of Biological Sciences (ICB) at the Federal University of Goiás (UFG), Brazil. After thawing the specimens were fixed and preserved in 10% aqueous formalin solution. Access to the abdominal cavity was carried out by an incision through the linea alba and removal of part of the pubis and pelvic symphysis. In order to dissect the ventral face of the lumbar and sacral regions, the colon, rectum, genitourinary organs, lumbar and sacral blood vessels, parietal peritoneum and pelvic fascia were removed. Subsequently, the ventral rami of the spinal nerves which form the sciatic and 1420 Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p , 2014
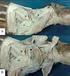
3 Anatomical aspects femoral nerves were dissected, and the pelvic limb skin was removed to allow access up to the branches responsible for the innervation of the leg and foot regions. All dissection stages were documented by drawings and digital images taken with a digital camera (Sony DSC-H50) and the terms were used in agreement with the Nomina Anatomica Veterinaria (International Committee on Veterinary Gross Anatomical Nomenclature, 2005). RESULTS The nerves which supply the leg and foot of the M. tridactyla were the saphenous (femoral nerve branch), common fibular, tibial and lateral sural cutaneous nerves (derived from the sciatic nerve) and the caudal sural cutaneous nerve (tibial nerve branch). After its origin, the saphenous nerve crosses through the femoral canal in the direction of the femoral triangle on the medial surface of the thigh. Throughout its course, it branches to the skin of this region and, after crossing the medial surface of the stifle joint, it reaches the leg, where it sprouts cranial and medial cutaneous branches to innervate the craniomedial surface of this segment (Figure 1A). Figure 1. A- Medial view of the thigh and leg of an adult M. tridactyla. Fe. Femoral nerve, crfe. Cutaneous ramus of the femoral nerve, S. Saphenous nerve and its lateral (lr) and medial (mr) rami, * Cutaneous ramus of the saphenous nerve. B and C- Dorsal view of the right foot of an adult M. tridactyla. F. Common fibular nerve, SF. Superficial fibular nerve and its medial (MR) and lateral (LR) rami, DF. Deep fibular nerve, S. Saphenous nerve and its lateral (lr) and medial (mr) rami, I-IV. Dorsal digital nerves I-IV, Medial proper dorsal digital nerve I. At the distal third of the leg, the saphenous nerve branches to the skin of the medial surface of the tarsus and metatarsus; distally to the tarsus, it splits into two branches: medial and lateral. The medial ramus emits the lateral dorsal digital nerve I, the dorsal common digital nerve I and a ramus to the dorsal common digital nerve II. The lateral ramus forms a plexiform structure at the dorsum of the foot, where it joins the medial ramus of the superficial fibular nerve. Branches from this plexus reinforce the common dorsal digital nerves I and II in both antimeres. However, in six antimeres (50%), it springs out a ramus to the dorsal common digital nerve III (ramus of the superficial fibular nerve) and in three antimeres (25%), it sends a ramus to the dorsal common digital nerve IV (Figure 1B and Table 1). The sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the sacral plexus of the M. tridactyla and is formed by the Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p ,
4 Cruz et al. last lumbar segment and the three or four first sacral segments. After its origin, it crosses the greater sciatic foramen in the distal direction and ends up splitting into the lateral sural cutaneous, common fibular and tibial nerves at the distal third of the thigh (Figure 2A). After arising from the sciatic nerve, the lateral sural cutaneous nerve follows the craniolateral fascia of the thigh between the femoral biceps and the femur, and splits into many rami which follow up to the craniolateral cutaneous region of the stifle joint and leg (Figure 2A). Table 1. Digital nerves of the foot of M. tridactyla Common fibular n. Tibial n. Saphenous n. Digit Surface SF MR LR DF MP LP MR LR I Dorsal II Dorsal III Dorsal (50%) IV Dorsal (25%) V Dorsal SF. Superficial fibular nerve, DF. Deep fibular nerve, MP. Medial plantar nerve, LP. Lateral plantar nerve, MR. Medial ramjus, LR. Lateral ramus. Figure 2. A- Lateral view of the distal extremity of the thigh and proximal extremity of the right leg of M. tridactyla. T. Tibial nerve, F. Common fibular nerve, LSC. Lateral sural cutaneous nerve, CSC. Caudal sural cutaneous nerve, 1. M. biceps femoris longus, 2. M. biceps femoris brevis. B- surface of the left foot of M. tridactyla. T. Tibial nerve, LP. Lateral plantar nerve, MP. Medial plantar nerve (Branches of the tibial nerve), I-IV. Common plantar digital nerves, V. lateral proper dorsal digital nerve V, 1. M. flexor brevis digiti, a. Tendon of the M. flexor pollicis brevis, b, c and d. Tendons of the M. flexor brevis digitorum, e. Tendon of the M. flexor digiti quinti brevis. Upon leaving the sciatic nerve at the distal third of the thigh, the common fibular nerve runs downward across the craniolateral surface of the thigh, where it becomes related to the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. Next, it crosses between the distal extremity of the femoral biceps and the proximal extremity of the lateral head of the gastrocnemius, emerging at the proximal third of 1422 Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p , 2014
5 Anatomical aspects the lateral surface of the leg, distally to the condyle of the fibula. It then dips between the long digital extensor and long fibular muscles. Throughout its course, it supplies the long and short fibular muscles, the cranial tibial and the long digital extensor muscles. The common fibular nerve splits into the superficial and deep fibular nerves at the level of the middle third of the leg. (Figure 1C). The superficial fibular nerve runs distally in contact with the lateral surface of the long digital extensor muscle and, in 50% of the cases, it splits into medial and lateral rami at the craniolateral surface of the tibiotarsal articulation. The other 50% split more distally at the proximal region of the metatarsus, where two rami are emitted. These rami establish connections in various ways to innervate the dorsal surface of the foot, making it difficult to establish a standard for the species. In general, the lateral ramus gives off the lateral proper dorsal digital nerve V and occasionally the dorsal common digital nerve IV. The medial ramus gives off cutaneous rami to the dorsum of the tarsus and metatarsus, and also branches to join rami of the saphenous nerve to form the dorsal common digital nerves II, III and IV (Figure 1C and Table 1). The deep fibular nerve runs cranially up to the tibia and the tibiotarsal joint, continuing deeply to the belly of the extensor hallucis longus, to which it branches and ends up dividing in the short digital extensor muscles. The tibial nerve is the main continuation of the sciatic nerve in its course through the distal third of the thigh. In the deep surface of the biceps femoris brevis muscle, it gives off the caudal sural cutaneous nerve (Figure 2A), responsible for the cutaneous innervation of the caudal surface of the leg. After sending the caudal sural cutaneous nerve, the tibial nerve extends distally between the medial and lateral heads of the gastrocnemius muscle reaching the caudomedial region of the leg. On its course, it branches to the gastrocnemius, plantar, soleus, long digital flexor, caudal tibial, flexor pollicis longus and popliteus muscles. After innervating the caudal musculature of the leg, the tibial nerve travels distally between the medial head of the gastrocnemius and the soleus muscles to the middle third of the leg, where it deviates medially and superficially while crossing the distal surface of the muscular belly of the medial head of the gastrocnemius. In this route, it runs alongside with the rete mirabile of the medial plantar artery and, at the middle third of the leg, springs out two branches to the skin of the caudal surface of the leg. At the distal third of the leg, the tibial nerve splits into medial and lateral plantar nerves, which are responsible for the innervation of the flexor digitorum brevis, quadratus plantae, flexor digiti V, abductor digiti V, abductor brevis digiti I, abductor metatarsal V, adductor brevis digiti I, adductor digiti II, flexor brevis digiti I, interossei and lumbricales muscles. On the plantar surface of the tarsometatarsal joint, the medial plantar nerve splits into three branches, which give off muscular branches and continue as common digital plantar nerves of the digits I, II and III (Figure 2B and Table 1). The lateral plantar nerve divides at the same level as the medial plantar nerve into the common digital plantar nerve IV and the proper plantar nerve V (Figure 2B and Table 1). Each digital nerve splits into the proper digital nerves at the level of the distal interphalangeal articulation. DISCUSSION There are many studies related to the origin and distribution of the sciatic and femoral nerves (Campos et al., 2003; Guimarães et al., 2005; Santos et al., 2006; Lima et al., 2008; Moraes et al., 2008; Aydin, 2009; Castro et al., 2009; Lizardo et al., 2009; Oliveira et al., 2010; Iglesias et al., 2011; Martinez-Pereira and Rickes, 2011; Oliveira et al., 2011; Pereira et al., 2011; Silva et al., 2011). However, the anatomy of the rami which branch from these nerves reaching the leg remains unknown in most of these species, since the authors rarely address the distribution of nerves distally to the knee. Possibly due to the difficulty in the dissection process, the cutaneous rami of the plantar and dorsal nerves of the foot are even less addressed, having been described in full only in the Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p ,
6 Cruz et al. porcupine (Aydin, 2009) and partially in the sea lion (Castro et al., 2009) and the chinchilla (Martinez-Pereira and Rickes, 2011). The nerves of the lumbosacral plexus responsible for the innervation of the foot and leg of the M. tridactyla were the saphenous, common fibular, tibial, caudal cutaneous sural and lateral cutaneous sural nerves, which coincides to reports in domestic (Getty, 1986; Schaller, 1999; Köning and Liebich 2004; Lorenz and Kornegay, 2006; Dyce et al., 2010) and wild animals (Erden, 1993; Aydin, 2009; Castro et al., 2009). The distribution of the saphenous nerve on the cranial and medial surface of the leg of the M. tridactyla was similar to that described in domestic animals (Getty, 1986; Lizardo et al., 2009; Dyce et al., 2010). Among wild animals, its distribution was addressed in the sea lion (Castro et al., 2009), in which the territory of innervation was restricted to the sural ventrolateral region, which differs from that observed in this study. A plexiform structure was formed by the saphenous and fibular nerves in the foot of the M. tridactyla, which is a feature also described in dogs and cats by Getty (1986). However, the author does not specify which digits the rami of this plexus lead to. In pigs, the same author reports that the saphenous nerve splits into lateral and medial rami at the distal third of the leg, as presented in this study. The lateral ramus joins the medial ramus of the superficial fibular nerve to form the dorsal common digital nerve II, while the medial ramus descends as the dorsal medial digital nerve II. In the M. tridactyla, apart from digit II, digits III and IV also receive branches from the saphenous nerve, which is not reported as a feature in any other species. The sciatic nerve in the M. tridactyla ends by dividing into the lateral sural cutaneous nerve, common fibular and tibial nerves. This division is more distal than that observed in domestic animals (Getty, 1986), in the sea lion (Castro et al., 2009) and in the crab-eating raccoon (Pereira et al., 2011), in which the ramification usually occurs after the sciatic nerve reaches the thigh or even in its middle third. The origin of the caudal sural cutaneous nerve varies among different species. In the M. tridactyla, as in the porcupine (Aydin, 2009), it arises from the tibial nerve. In dogs and bovines (Getty, 1986), sea lions (Castro et al., 2009) and in the chinchilla (Martinez-Pereira and Rickes, 2011), it arises directly from the sciatic nerve. The same occurs with the origin of the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. It branches directly from the sciatic nerve in dogs (Getty, 1986) and in the chinchilla (Martinez-Pereira and Rickes, 2011), as observed in this study. On the other hand, Aydin (2009) in the porcupine, Schaller (1999), König and Liebich (2004) and Dyce et al. (2010), in domestic animals, describe it as a branch of the common fibular nerve. The division of the common fibular nerve into superficial and deep fibular nerves occurs as soon as the common fibular nerve emerges in the leg (Getty, 1986; Schaller, 1999; König and Liebich, 2004; Castro et al., 2009). Nevertheless, in the M. tridactyla this division takes place at the level of the middle third of the leg. As a consequence, the craniolateral muscles of the leg of the M. tridactyla are innervated by branches directly from the common fibular nerve, not by branches from the superficial and deep fibular nerves as in other species. The muscular rami that branch directly off the common fibular nerve in the M. tridactyla were addressed to the long fibular, short fibular, cranial tibial and long digital extensor muscles, which are all innervated by the deep fibular nerve in domestic animals (Getty, 1986). Therefore, the deep fibular nerve in the M. tridactyla only innervates two muscles: the extensor hallucis longus and the extensor digitorum brevis. The lateral digital extensor muscle and the fifth fibular muscle are mentioned by Schaller (1999) and Castro et al. (2009), respectively, as innervated by the superficial fibular nerve, but they are absent in the M. tridactyla. Apart from the motor innervation of the tarsal flexor and digital extensor muscles, Miller (1964) and Dyce et al. (2010) also mention the sensitive innervation of the foot structures. It is intermediated by the union of dorsal metatarsal structures derived from the deep fibular nerve with dorsal digital rami, which in turn are derived from the superficial fibular nerve. This 1424 Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p , 2014
7 Anatomical aspects does not occur in the M. tridactyla, since the deep fibular nerve does not send dorsal metatarsal branches. In the M. tridactyla, the tibial nerve innervates the gastrocnemius, plantar, soleus, long flexor of the digits, caudal tibial, flexor hallucis longus and popliteus muscles, in accordance to that described in humans (Gilroy et al., 2008). This is possibly due to the muscular similarity between these two species. The division of the tibial nerve into medial and lateral plantar nerves corroborates the pattern described in the other species (Miller, 1964; Getty, 1986; König and Liebich, 2004; Gilroy et al., 2008; Dyce et al., 2010). However, the formation of the digital nerves is directly correlated to the number of digits in such a manner that the distal distribution of this nerve was closer to that reported in animals with a larger number of digits, such as carnivores. Thus, the ramification of the medial and the lateral plantar nerves for the formation of the common digital nerves was in accordance to what Schaller (1999) described in swine. Nonetheless, Miller (1964) and Schaller (1999) described the plantar digital nerves in dogs as derived from the lateral plantar nerve since the two join to form the common digital nerve. This was not observed in the M. tridactyla. In conclusion, the nerves responsible for the innervation of the leg and foot of the M. tridactyla were the same as those reported in domestic and wild animals with a few differences. The division of the common fibular nerve is more distal, which results in significant differences in the innervation of the leg muscles in relation to the standard described in domestic animals. The absence of dorsal metatarsal branches of the deep fibular nerve to innervate the dorsum of the foot was recorded. The participation of the saphenous nerve in the digital innervation is more effective, also contributing with branches to the digits III and IV, apart from the digits I and II. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors would like to thank IBAMA - Brazilian Institute of Environment and Renewable Natural Resources for donating the M. tridactyla specimens used in this study. REFERENCES AYDIN, A. The dissemination of the pelvic limb nerves originating from the lumbosacral plexus in the porcupine (Hystrix cristata). Vet. Med-Cezech, v.54, p , BRAGA, F.G. Plano de conservação para tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla). In: BRAGA, F.G. Instituto Ambiental do Paraná, Planos de ação para Espécies de mamíferos ameaçados. IAP: Curitiba, p BARRETO, A. Tamanduás-bandeira e sua vulnerabilidade. Clin. Vet., v.68, p.12-16, CAMPOS, D.B.; SILVA, F.O.C.; SEVERINO R.S. et al. Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos em fetos de bovinos azebuados. Ars Vet., v.19, p , CASTRO, T.F.; SOUZA, D.A.S.; SILVA FILHO, R.P.; PEREIRA, M.A.M. Sistematização e distribuição da inervação lombar e sacral em Arctocephalus australis. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci., v.46, p , DYCE, K.M.; SACK, W.O.; WENSING, C.J.G. Tratado de anatomia veterinária, 4.ed. Rio de Janeiro: Editora Elsevier, p. ERDEN, H. Merkebin (equus asinus l.) plexus lumbosacralis'i üzerinde makroanatomik ve subgros çalişmalar. S. Ü. Vet. Fak. Derg., v.9, p.64-71, GETTY, R. Anatomia dos animais domésticos. 5.ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, p. GILROY, A.M.; MACPHERSON, B.R.; ROSS L.M. Atlas de Anatomia. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, p. GUIMARÃES, G.C.; MACHADO, M.R.F.; SANTOS, A.L.Q. et al. Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático no gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnareus, 1758), Biosci. J., v.21, p , IGLESIAS, L.P.; SILVA, F.O.C.; BRITO. T.R. Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em fetos de javalis (Sus scrofa scrofa). Biotemas, v.24, p , Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p ,
8 Cruz et al. INTERNATIONAL COMMITTEE ON VETERINARY GROSS ANATOMICAL NOMENCLATURE. Nomina anatomica veterinaria. 5.ed. Ithaca: Cornell University, p. IUCN, Red List of Threatened Species. Version Disponível em: <http// Acessado em: 26 Ago KÖNIG, H.E.; LIEBICH, H.J. Anatomia dos animais domésticos. Porto Alegre: Artmed, v.2, p. LIMA, E.M.M.; SILVA, F.O.C.; SEVERINO, R.S. et al. Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos em caprinos da raça Saanen. Cienc. Rural, v.38, p , LIZARDO, F.B.; SILVA, F.O.C.; SEVERINO, R.S. et al. Origin and distribution of the femoral nerve in fetuses of zebu-crossed bovines. Braz. J. Morphol. Sci., v.26, p.91-96, LORENZ, M.D.; KORNEGAY, J.N. Neurologia Veterinária. 2.ed. Barueri: Manole, p. MARTINEZ-PEREIRA, M.A.; RICKES, E.M. The spinal nerves that constitute the lumbosacral plexus and their distribution in the chinchilla. J. S. Afri. Vet. Ass., v.82, p , MILLER, M.E. Anatomy of the dog. Philadelphia: W. B. Saunders, p. MORAES, D.V.; MARTINS, J.D.; SILVA, F.O.C. et al. Origem e distribuição do nervo femoral em equinos sem raça definida. Rev. Hor. Cient., v.1, p.1-10, MOURÃO, G.; MEDRI, M. Activity of a specialized insectivorous mammal (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) in the Pantanal of Brazil. J. Zool., v.271, p , OLIVEIRA, G.B.; RODRIGUES, M.N.; SOUSA, E.S. et al. Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos do preá. Cienc. Rural, v.40, p , OLIVEIRA, G.B.; ALBUQUERQUE, J.F.G.; RODRIGUES, M.N. et al. Origem e distribuição do nervo femoral em mocó, Kerodon rupestris (Cavidae). Pesq. Vet. Bras., v.31, p.84-88, PEREIRA, K.F.; PARANAIBA, J.F.F.S.; HELRIGLE, C.; ARAÚJO, E.G. Origem e distribuição anatômica do nervo isquiático de mão-pelada. Pesq. Vet. Bras., v.31, p.74-78, SANTOS, R.C.; ALBUQUERQUE, J.F.G.; SILVA, M.C.V. et al. Anatomia do nervo isquiático em mocós (Kerodon rupestris WIED, 1820) aplicada a clínica de animais silvestres. Braz. J. Vet. Res. Anim. Sci., v.43, p , SCHALLER, O. Nomenclatura anatômica veterinária ilustrada. São Paulo: Manole, p. SHAW, J.H.; MACHADO-NETO, J.; CARTER, T.S. Behavior of free-living giant anteaters (Myrmecophaga tridactyla). Biotropica, v.19, p , SILVA, F.O.C.; BRITO, T.R.; VASCONCELOS, B.G. et al. Origens e distribuições dos nervos femorais em ovinos sem raça definida. Biosci. J., v.27, p , SILVEIRA, L.; RODRIGUES, F.H.G.; JACOMO, A.T.D.; DINIZ, J.H.F. Impact of wildfires on the megafauna of Emas National Park, central Brazil. Oryx, v.33, p , VIZCAÍNO, S.F.; LOUGHRY, W.J. The Biology of the enarthra. Gainesville: University Press of Florida, p Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.66, n.5, p , 2014
Antônio Rodrigues de Araújo NETO¹, Eros Jofily Fernandes Soares ARAÚJO¹, Ayrton Senna Barbosa da SILVA¹, Danila Barreiro CAMPOS²
 ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE ISCHIADICUM NERVE IN BROWN THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS,
ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE ISCHIADICUM NERVE IN BROWN THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS,
ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE TAMANDUÁ- BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758)
 Original Article 1275 ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE TAMANDUÁ- BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758) ANATOMICAL ASPECTS OF THE NERVES OF THE THIGH OF THE GIANT ANTEATER (Myrmecophaga
Original Article 1275 ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE TAMANDUÁ- BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus, 1758) ANATOMICAL ASPECTS OF THE NERVES OF THE THIGH OF THE GIANT ANTEATER (Myrmecophaga
Eros Jofily Fernandes Soares ARAÚJO¹, Ayrton Senna Barbosa da SILVA¹, Antônio Rodrigues de Araújo NETO¹, Danila Barreiro CAMPOS ²
 ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO FEMORAL EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ, 1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FEMORAL NERVE IN BROWN-THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,
ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO FEMORAL EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ, 1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE FEMORAL NERVE IN BROWN-THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,
Ayrton Senna Barbosa da SILVA 1, Antônio Rodrigues de Araújo NETO 1, Eros Jofily Fernandes Soares ARAÚJO 1, Danila Barreiro CAMPOS 2
 ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO OBTURADOR EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE OBTURATOR NERVE IN BROWN- THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS,
ORIGEM E DESCRIÇÃO DO NERVO OBTURADOR EM BICHO-PREGUIÇA-DE- GARGANTA-MARROM (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS, SCHINZ,1825) ORIGIN AND DESCRIPTION OF THE OBTURATOR NERVE IN BROWN- THROATED SLOTH (BRADYPUS VARIEGATUS,
Origens, distribuições e ramificações dos nervos femorais no tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla Linnaeus, 1758)
 Biotemas, 26 (4): 161-166, dezembro de 2013 ISSNe 2175-7925 161 http://dx.doi.org/10.5007/2175-7925.2013v26n4p161 Origens, distribuições e ramificações dos nervos femorais no tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga
Biotemas, 26 (4): 161-166, dezembro de 2013 ISSNe 2175-7925 161 http://dx.doi.org/10.5007/2175-7925.2013v26n4p161 Origens, distribuições e ramificações dos nervos femorais no tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga
Descrição anatômica dos músculos da perna de Procyon cancrivorus (Cuvier 1798)
 Biotemas, 23 (3): 159-165, setembro de 2010 ISSN 0103 1643 159 Descrição anatômica dos músculos da perna de Procyon cancrivorus (Cuvier 1798) Firmino Cardoso Pereira* Vanessa Morais Lima Kleber Fernando
Biotemas, 23 (3): 159-165, setembro de 2010 ISSN 0103 1643 159 Descrição anatômica dos músculos da perna de Procyon cancrivorus (Cuvier 1798) Firmino Cardoso Pereira* Vanessa Morais Lima Kleber Fernando
DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO FIBULAR COMUM EM FETOS DE EQUINOS (SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA) E DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DE PONTOS PARA BLOQUEIO ANESTÉSICO
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO FIBULAR COMUM EM FETOS DE EQUINOS (SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA) E DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DE PONTOS PARA BLOQUEIO ANESTÉSICO
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO FIBULAR COMUM EM FETOS DE EQUINOS (SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA) E DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DE PONTOS PARA BLOQUEIO ANESTÉSICO
ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS E FUNCIONAIS DOS MÚSCULOS MEDIAIS DA COXA DO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla)
 ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS E FUNCIONAIS DOS MÚSCULOS MEDIAIS DA COXA DO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Viviane Souza CRUZ 1 ; Júlio Roquete CARDOSO 1 ; Marcelo Seixo de Brito e SILVA 1 ; Gustavo
ASPECTOS ANATÔMICOS E FUNCIONAIS DOS MÚSCULOS MEDIAIS DA COXA DO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Viviane Souza CRUZ 1 ; Júlio Roquete CARDOSO 1 ; Marcelo Seixo de Brito e SILVA 1 ; Gustavo
Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em fetos de javalis (Sus scrofa scrofa)
 Biotemas, 24 (4): 141-145, dezembro de 2011 ISSNe 2175-7925 141 doi: 10.5007/2175-7925.2011v24n4p141 Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em fetos de javalis (Sus scrofa scrofa) Luciana Pedrosa Iglesias¹*
Biotemas, 24 (4): 141-145, dezembro de 2011 ISSNe 2175-7925 141 doi: 10.5007/2175-7925.2011v24n4p141 Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em fetos de javalis (Sus scrofa scrofa) Luciana Pedrosa Iglesias¹*
Estudo anatômico do plexo lombossacral de Tamandua tetradactyla
 Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.65, n.6, p.1720-1728, 2013 Estudo anatômico do plexo lombossacral de Tamandua tetradactyla [Anatomical study of the lumbosacral plexus of the Tamandua tetradactyla] J.R.
Arq. Bras. Med. Vet. Zootec., v.65, n.6, p.1720-1728, 2013 Estudo anatômico do plexo lombossacral de Tamandua tetradactyla [Anatomical study of the lumbosacral plexus of the Tamandua tetradactyla] J.R.
Anatomia do músculo abdutor crural caudal do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758)
 723 Anatomia do músculo abdutor crural caudal do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758) Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 1 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 1 André Luiz Quagliatto SANTOS 2 Maria
723 Anatomia do músculo abdutor crural caudal do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758) Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 1 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 1 André Luiz Quagliatto SANTOS 2 Maria
Universidade de Brasília. Faculdade de Agronomia e Medicina Veterinária. Programa de pós-graduação em Saúde Animal
 Universidade de Brasília Faculdade de Agronomia e Medicina Veterinária Programa de pós-graduação em Saúde Animal ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM OVINOS DA RAÇA SANTA INÊS REGINALDO BOMFIM
Universidade de Brasília Faculdade de Agronomia e Medicina Veterinária Programa de pós-graduação em Saúde Animal ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM OVINOS DA RAÇA SANTA INÊS REGINALDO BOMFIM
ORIGENS E RAMIFICAÇÕES DO NERVO FEMORAL EM JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758)
 Original Article 727 ORIGENS E RAMIFICAÇÕES DO NERVO FEMORAL EM JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758) ORIGINS AND RAMIFICATIONS OF THE FEMORAL NERVE IN WILD BOARS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758)
Original Article 727 ORIGENS E RAMIFICAÇÕES DO NERVO FEMORAL EM JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758) ORIGINS AND RAMIFICATIONS OF THE FEMORAL NERVE IN WILD BOARS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758)
Origem e distribuição anatômica do nervo isquiático de mão-pelada (Procyon
 Origem e distribuição anatômica do nervo isquiático de mão-pelada 1 Kleber F. Pereira 2*, Juliana F.F.e S. Paranaiba 2, Carla Helrigle 2 e Eugênio G. de Araújo 3 ABSTRACT.- Pereira K.F., Paranaiba J.F.F.S.,
Origem e distribuição anatômica do nervo isquiático de mão-pelada 1 Kleber F. Pereira 2*, Juliana F.F.e S. Paranaiba 2, Carla Helrigle 2 e Eugênio G. de Araújo 3 ABSTRACT.- Pereira K.F., Paranaiba J.F.F.S.,
ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO ANTIMÉRICA DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS EM CAPRINOS RECÉM-NATOS DA RAÇA SAANEN
 DOI: 10.1590/1089-6891v16i225290 MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO ANTIMÉRICA DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS EM CAPRINOS RECÉM-NATOS DA RAÇA SAANEN ORIGIN AND ANTIMERIC DISTRIBUTION OF THE FEMORAL NERVES
DOI: 10.1590/1089-6891v16i225290 MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO ANTIMÉRICA DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS EM CAPRINOS RECÉM-NATOS DA RAÇA SAANEN ORIGIN AND ANTIMERIC DISTRIBUTION OF THE FEMORAL NERVES
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGENS, DISTRIBUIÇÕES E RAMIFICAÇÕES DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS NO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla LINNAEUS, 1758) Tharlianne Alici
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGENS, DISTRIBUIÇÕES E RAMIFICAÇÕES DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS NO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla LINNAEUS, 1758) Tharlianne Alici
ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS ISQUIÁTICOS EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS
 ARS VETERINARIA, ISSN 0102-6380 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS ISQUIÁTICOS EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS (ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE ISCHIATIC NERVES IN FETUSES OF THE CROSSBRED ZEBU CATTLE) D. B.
ARS VETERINARIA, ISSN 0102-6380 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS ISQUIÁTICOS EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS (ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE ISCHIATIC NERVES IN FETUSES OF THE CROSSBRED ZEBU CATTLE) D. B.
DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA. DO CACHORRO-DO-MATO (Cerdocyon thous)
 DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA DO CACHORRO-DO-MATO (Cerdocyon thous) ANATOMICAL DESCRIPTION OF LEG MUSCLES OF CACHORRO-DO-MATO (Cerdocyon thous) BORDIGNON, Heloísa Laís Fialkowski Acadêmica
DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA DO CACHORRO-DO-MATO (Cerdocyon thous) ANATOMICAL DESCRIPTION OF LEG MUSCLES OF CACHORRO-DO-MATO (Cerdocyon thous) BORDIGNON, Heloísa Laís Fialkowski Acadêmica
Anatomia Comparativa dos nervos do membro pélvico de Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al. 2000)
 Anatomia Comparativa dos nervos do membro pélvico de Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al. 2000) Giovanna Felipe Cavalcante 1 ; Tales Alexandre Aversi-Ferreira 2 1 Aluno do Curso de Enfermagem; Campus de Palmas;
Anatomia Comparativa dos nervos do membro pélvico de Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al. 2000) Giovanna Felipe Cavalcante 1 ; Tales Alexandre Aversi-Ferreira 2 1 Aluno do Curso de Enfermagem; Campus de Palmas;
e a distribuição do nervo isquiático no veado-catingueiro (Mazama gouazoubira) 1
 Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático no veado-catingueiro (Mazama gouazoubira) 1 Tracy Martina M. Martins 2, Kleber F. Pereira 2, Fabiano Campos Lima 2, André L.Q. Santos 3 e Taís Malysz 2 * ABSTRACT.-
Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático no veado-catingueiro (Mazama gouazoubira) 1 Tracy Martina M. Martins 2, Kleber F. Pereira 2, Fabiano Campos Lima 2, André L.Q. Santos 3 e Taís Malysz 2 * ABSTRACT.-
Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET102 Anatomia dos Animais Domésticos
 Catálogo de Graduação 016 da UFV 0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET10 Anatomia dos Animais Domésticos Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 4 Teóricas
Catálogo de Graduação 016 da UFV 0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET10 Anatomia dos Animais Domésticos Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 4 Teóricas
sumária e apresenta, inclusive, algumas controvérsias. Nickel et al. (1981) citam que este músculo é bem saliente no gato e freqüentemente ausente no
 Original Article PRESENÇA DO MÚSCULO BRAQUIORRADIAL EM CÃES PRESENCE OF THE BRAQUIORRADIAL MUSCLE OF DOGS Ivaldo dos SANTOS JÚNIOR * Celso Alves RODRIGUES ** Aglai CAMPOS * Djenane dos SANTOS *** RESUMO:
Original Article PRESENÇA DO MÚSCULO BRAQUIORRADIAL EM CÃES PRESENCE OF THE BRAQUIORRADIAL MUSCLE OF DOGS Ivaldo dos SANTOS JÚNIOR * Celso Alves RODRIGUES ** Aglai CAMPOS * Djenane dos SANTOS *** RESUMO:
AVALIAR A ANATOMIA DE SUPERFÍCIE DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO DO CÃO.
 AVALIAR A ANATOMIA DE SUPERFÍCIE DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO DO CÃO. Orientar o membro em relação a sua posição in vivo. Usando os esqueletos da sala de dissecação, como auxílio, orientar o membro e decidir se você
AVALIAR A ANATOMIA DE SUPERFÍCIE DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO DO CÃO. Orientar o membro em relação a sua posição in vivo. Usando os esqueletos da sala de dissecação, como auxílio, orientar o membro e decidir se você
Eixos e Planos de Construção do Corpo de Vertebrados
 Universidade Federal do Acre Curso de Medicina Veterinária Eixos e Planos de Construção do Corpo de Vertebrados Prof. Adj. Dr. Yuri Karaccas de Carvalho Anatomia Descritiva Animal I Objetivos da Aula Introdução
Universidade Federal do Acre Curso de Medicina Veterinária Eixos e Planos de Construção do Corpo de Vertebrados Prof. Adj. Dr. Yuri Karaccas de Carvalho Anatomia Descritiva Animal I Objetivos da Aula Introdução
DESCRIÇÃO DOS TERRITÓRIOS NERVOSOS E MUSCULATURA DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO EM Puma concolor
 DESCRIÇÃO DOS TERRITÓRIOS NERVOSOS E MUSCULATURA DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO EM Puma concolor EBONE, Christian 1 ; BRITO, Matheus Cândano 2 ; WILGES, Carlos Henrique de Mello 3 ; SILVA, Aline Alves 3, MARTINEZ-PEREIRA,
DESCRIÇÃO DOS TERRITÓRIOS NERVOSOS E MUSCULATURA DO MEMBRO PÉLVICO EM Puma concolor EBONE, Christian 1 ; BRITO, Matheus Cândano 2 ; WILGES, Carlos Henrique de Mello 3 ; SILVA, Aline Alves 3, MARTINEZ-PEREIRA,
Universidade Federal do Acre Curso de Medicina Veterinária
 Universidade Federal do Acre Curso de Medicina Veterinária Sistema Circulatório II Artérias Prof. Adj. Dr. Yuri Karaccas de Carvalho Anatomia Descritiva Animal I 1 Objetivos da Aula Diferenciar: Veia X
Universidade Federal do Acre Curso de Medicina Veterinária Sistema Circulatório II Artérias Prof. Adj. Dr. Yuri Karaccas de Carvalho Anatomia Descritiva Animal I 1 Objetivos da Aula Diferenciar: Veia X
Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos do preá
 Ciência Rural, Santa Maria, v.40, n.8, Origem p.1741-1745, e distribuição ago, 2010 dos nervos isquiáticos do preá. ISSN 0103-8478 1741 Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos do preá Origin and distribuition
Ciência Rural, Santa Maria, v.40, n.8, Origem p.1741-1745, e distribuição ago, 2010 dos nervos isquiáticos do preá. ISSN 0103-8478 1741 Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos do preá Origin and distribuition
PUBVET, Publicações em Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia.
 PUBVET, Publicações em Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. Músculos da face lateral e medial da pelve e da coxa de Coendou prehensilis (Linnaeus, 1758) (Rodentia, Erethizontidae) André Luiz Quagliatto Santos
PUBVET, Publicações em Medicina Veterinária e Zootecnia. Músculos da face lateral e medial da pelve e da coxa de Coendou prehensilis (Linnaeus, 1758) (Rodentia, Erethizontidae) André Luiz Quagliatto Santos
Ramificação e distribuição dos nervos frênicos no músculo diafragma do gato doméstico
 290 Ramificação e distribuição dos nervos frênicos no músculo diafragma do gato doméstico Pamela Rodrigues Reina MOREIRA 1 Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 2 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 2 André Luiz Quagliatto
290 Ramificação e distribuição dos nervos frênicos no músculo diafragma do gato doméstico Pamela Rodrigues Reina MOREIRA 1 Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 2 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 2 André Luiz Quagliatto
ORIGENS E DISTRIBUIÇÕES DO NERVO OBTURATÓRIO EM FETOS DE JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEU 1758)
 Original Article 527 ORIGENS E DISTRIBUIÇÕES DO NERVO OBTURATÓRIO EM FETOS DE JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEU 1758) ORIGINS AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE OBTURATORIUS NERVE IN WILD BOARS FETUSES (Sus scrofa
Original Article 527 ORIGENS E DISTRIBUIÇÕES DO NERVO OBTURATÓRIO EM FETOS DE JAVALIS (Sus scrofa scrofa LINNAEU 1758) ORIGINS AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE OBTURATORIUS NERVE IN WILD BOARS FETUSES (Sus scrofa
Palavras-chave: Animais selvagens, linfonodos, Xenarthra, Myrmecophagidae. Keywords: Wild animals, lymph nodes, Xenarthra, Myrmecophagidae.
 1 ASPECTOS MORFOLÓGICOS DOS LINFOCENTROS SUPERFICIAIS DA CABEÇA E PESCOÇO DE Myrmecophaga tridactyla Brunna Rocha ADORNO 1 ; Viviane de Souza CRUZ 2 ; Flávio de Resende GUIMARÃES 3, Paulo César MOREIRA
1 ASPECTOS MORFOLÓGICOS DOS LINFOCENTROS SUPERFICIAIS DA CABEÇA E PESCOÇO DE Myrmecophaga tridactyla Brunna Rocha ADORNO 1 ; Viviane de Souza CRUZ 2 ; Flávio de Resende GUIMARÃES 3, Paulo César MOREIRA
Origem e distribuição antimérica dos nervos obturatórios em caprinos neonatos da raça Saanen*
 74 http://dx.doi.org/10.4322/rbcv.2014.057 Origem e distribuição antimérica dos nervos obturatórios em caprinos neonatos da raça Saanen* Origin and antimeric distribution of the obturator nerves in newborns
74 http://dx.doi.org/10.4322/rbcv.2014.057 Origem e distribuição antimérica dos nervos obturatórios em caprinos neonatos da raça Saanen* Origin and antimeric distribution of the obturator nerves in newborns
DISTRIBUIÇÀO ANTIMÉRICA DO MÚSCULO BRAQUIORRADIAL EM CÃES SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA
 55 DISTRIBUIÇÀO ANTIMÉRICA DO MÚSCULO BRAQUIORRADIAL EM CÃES SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA FERNANDA MARQUES PESTANA 1 BÁRBARA XAVIER SILVA 2 MAURÍCIO ALVES CHAGAS 3 MÁRCIO ANTÔNIO BABINSKI 3 MARCELO ABIDU-FIGUEIREDO
55 DISTRIBUIÇÀO ANTIMÉRICA DO MÚSCULO BRAQUIORRADIAL EM CÃES SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA FERNANDA MARQUES PESTANA 1 BÁRBARA XAVIER SILVA 2 MAURÍCIO ALVES CHAGAS 3 MÁRCIO ANTÔNIO BABINSKI 3 MARCELO ABIDU-FIGUEIREDO
Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET101 Anatomia Veterinária I
 0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 8 Teóricas Práticas Total Duração em semanas: 15 Carga horária semanal 6 8
0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 8 Teóricas Práticas Total Duração em semanas: 15 Carga horária semanal 6 8
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA PAULO ANTÔNIO MOREIRA SANTOS LEMOS REZENDE
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA PAULO ANTÔNIO MOREIRA SANTOS LEMOS REZENDE ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus - LINNAEUS, 1758) DA LINHAGEN DAN BRED
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA PAULO ANTÔNIO MOREIRA SANTOS LEMOS REZENDE ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus - LINNAEUS, 1758) DA LINHAGEN DAN BRED
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ASPECTOS EVOLUTIVOS SOBRE AS ORIGENS, DISTRIBUIÇÕES E RAMIFICAÇÕES DOS NERVOS ISQUIÁTICOS DO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ASPECTOS EVOLUTIVOS SOBRE AS ORIGENS, DISTRIBUIÇÕES E RAMIFICAÇÕES DOS NERVOS ISQUIÁTICOS DO TAMANDUÁ BANDEIRA (Myrmecophaga tridactyla
MORFOLOGIA DO PLEXO LOMBOSACRO DE UM EXEMPLAR DE VEADO CATINGUEIRO (MAZAMA GOUAZOUBIRA, FISCHER, 1814) 1 MORPHOLOGY OF A SPECIMEN OF BROCKET DEER
 MORFOLOGIA DO PLEXO LOMBOSACRO DE UM EXEMPLAR DE VEADO CATINGUEIRO (MAZAMA GOUAZOUBIRA, FISCHER, 1814) 1 MORPHOLOGY OF A SPECIMEN OF BROCKET DEER Bruna Eduarda Riquinho 2, Bruna Carolina Ulsenheimer 3,
MORFOLOGIA DO PLEXO LOMBOSACRO DE UM EXEMPLAR DE VEADO CATINGUEIRO (MAZAMA GOUAZOUBIRA, FISCHER, 1814) 1 MORPHOLOGY OF A SPECIMEN OF BROCKET DEER Bruna Eduarda Riquinho 2, Bruna Carolina Ulsenheimer 3,
Características anatômicas do plexo braquial de tamanduá-mirim (Tamandua tetradactyla Linnaeus, 1758)
 Características anatômicas do plexo braquial de tamanduá-mirim (Tamandua tetradactyla Linnaeus, 1758) Anatomical characteristics of the brachial plexus of lesser anteater ( Tamandua tetradactyla Linnaeus,
Características anatômicas do plexo braquial de tamanduá-mirim (Tamandua tetradactyla Linnaeus, 1758) Anatomical characteristics of the brachial plexus of lesser anteater ( Tamandua tetradactyla Linnaeus,
DESCRIPTION OF TERMINAL RAMIFICATIONS OF THE ABDOMINAL AORTA IN DOGS (Canis familiaris)
 REVISTA CIENTÍFICA DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA - ISSN 1679-7353 Ano XV - Número 31 JULHO de 2018 Periódico Semestral DESCRIPTION OF TERMINAL RAMIFICATIONS OF THE ABDOMINAL AORTA IN DOGS (Canis familiaris)
REVISTA CIENTÍFICA DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA - ISSN 1679-7353 Ano XV - Número 31 JULHO de 2018 Periódico Semestral DESCRIPTION OF TERMINAL RAMIFICATIONS OF THE ABDOMINAL AORTA IN DOGS (Canis familiaris)
FORMAÇÃO DA VEIA PORTA E DE SUAS TRIBUTÁRIAS EM GATOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758)
 Original Article 112 FORMAÇÃO DA VEIA PORTA E DE SUAS TRIBUTÁRIAS EM GATOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758) PORTAL VEIN AND ITS TRIBUTARIES FORMATION IN CATS WITHOUT DEFINED BREED (Felis
Original Article 112 FORMAÇÃO DA VEIA PORTA E DE SUAS TRIBUTÁRIAS EM GATOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA (Felis catus Linnaeus, 1758) PORTAL VEIN AND ITS TRIBUTARIES FORMATION IN CATS WITHOUT DEFINED BREED (Felis
Anatomia do nervo isquiático em mocós (Kerodon rupestris WIED, 1820) aplicada a clínica de animais silvestres
 647 Anatomia do nervo isquiático em mocós (Kerodon rupestris WIED, 1820) aplicada a clínica de animais silvestres Renata Celis dos SANTO José Fernando Gomes de ALBUQUERQUE 2 Márcio César Vasconcelos SILVA
647 Anatomia do nervo isquiático em mocós (Kerodon rupestris WIED, 1820) aplicada a clínica de animais silvestres Renata Celis dos SANTO José Fernando Gomes de ALBUQUERQUE 2 Márcio César Vasconcelos SILVA
JOSÉ RICARDO SANCHEZ FILHO ANALYSIS OF THE LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF THE VOLUNTARY OFFER OF THE BID RULE ON STOCKS LISTED IN THE BRAZILIAN STOCK EXCHANGE
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DO RIO DE JANEIRO INSTITUTO COPPEAD DE ADMINISTRAÇÃO JOSÉ RICARDO SANCHEZ FILHO ANALYSIS OF THE LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF THE VOLUNTARY OFFER OF THE BID RULE ON STOCKS LISTED IN THE BRAZILIAN
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DO RIO DE JANEIRO INSTITUTO COPPEAD DE ADMINISTRAÇÃO JOSÉ RICARDO SANCHEZ FILHO ANALYSIS OF THE LONG-TERM EFFECTS OF THE VOLUNTARY OFFER OF THE BID RULE ON STOCKS LISTED IN THE BRAZILIAN
Acadêmica do curso de Medicina Veterinária da UNIJUÍ - 3
 ORIGENS E RAMIFICAÇÕES DO PLEXO BRAQUIAL EM UM EXEMPLAR DE GAMBÁ DE ORELHA BRANCA (DIDELPHIS ALBIVENTRIS LUND, 1841) 1 BRACHIAL PLEXUS ORIGINS AND BRANCHES IN AN EXEMPLARY OF EAR WHITE SKUNK (DIDELPHIS
ORIGENS E RAMIFICAÇÕES DO PLEXO BRAQUIAL EM UM EXEMPLAR DE GAMBÁ DE ORELHA BRANCA (DIDELPHIS ALBIVENTRIS LUND, 1841) 1 BRACHIAL PLEXUS ORIGINS AND BRANCHES IN AN EXEMPLARY OF EAR WHITE SKUNK (DIDELPHIS
Origem e distribuição do nervo femoral do mocó, Kerodon rupestris (Cavidae) 1
 Pesq Vet Bras (Supl):8-88, dezembro Origem e distribuição do nervo femoral do mocó, Kerodon rupestris (Cavidae) Gleidson B Oliveira, José FG Albuquerque, Marcio N Rodrigues, ALC Paiva, Carlos EB Moura,
Pesq Vet Bras (Supl):8-88, dezembro Origem e distribuição do nervo femoral do mocó, Kerodon rupestris (Cavidae) Gleidson B Oliveira, José FG Albuquerque, Marcio N Rodrigues, ALC Paiva, Carlos EB Moura,
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA GUSTAVO CAVINATO HERRERA
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA GUSTAVO CAVINATO HERRERA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS EM FETOS SUÍNOS (SUS SCROFA DOMESTICUS - LINNEAUS, 1758) DO CRUZAMENTO DAS LINHAGENS DAN BRED E AGPIC337
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA GUSTAVO CAVINATO HERRERA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS FEMORAIS EM FETOS SUÍNOS (SUS SCROFA DOMESTICUS - LINNEAUS, 1758) DO CRUZAMENTO DAS LINHAGENS DAN BRED E AGPIC337
Dyce, Sack e Wensing (2004), em equinos, Ghoshal (1986c), em suínos, Lacerda et al. (2006), em mocós, Ferraz et al. (2006), em fetos de bovinos
 26 V. DISCUSSÃO Ferraz et al. (2006) relataram que é muito provável que o nervo isquiático apresente no adulto, origem e sintopia semelhante ao que foi encontrado em fetos de bovinos azebuados, acreditamos
26 V. DISCUSSÃO Ferraz et al. (2006) relataram que é muito provável que o nervo isquiático apresente no adulto, origem e sintopia semelhante ao que foi encontrado em fetos de bovinos azebuados, acreditamos
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA. DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al.
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al., 2000) Kliver Antonio Marin Fisioterapeuta UBERLÂNDIA MINAS GERAIS
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DISTRIBUIÇÃO DOS NERVOS DA COXA DE Cebus libidinosus (Rylands et al., 2000) Kliver Antonio Marin Fisioterapeuta UBERLÂNDIA MINAS GERAIS
ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO RETAL CAUDAL EM EQUINOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE CAUDAL RECTAL NERVE IN MIXED BREED HORSES
 Original Article 1496 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO RETAL CAUDAL EM EQUINOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE CAUDAL RECTAL NERVE IN MIXED BREED HORSES Thalita Rocha BRITO 1 ; Bruno Gomes
Original Article 1496 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO RETAL CAUDAL EM EQUINOS SEM RAÇA DEFINIDA ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE CAUDAL RECTAL NERVE IN MIXED BREED HORSES Thalita Rocha BRITO 1 ; Bruno Gomes
Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos em caprinos da raça Saanen
 Ciência 372 Rural, Santa Maria, v.38, n.2, p.372-377, mar-abr, 2008 Lima et al. ISSN 0103-8478 Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos em caprinos da raça Saanen Origin and distribution of the ischiatic
Ciência 372 Rural, Santa Maria, v.38, n.2, p.372-377, mar-abr, 2008 Lima et al. ISSN 0103-8478 Origem e distribuição dos nervos isquiáticos em caprinos da raça Saanen Origin and distribution of the ischiatic
Universidade Federal de Uberlândia Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária
 Universidade Federal de Uberlândia Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária ORIGEM DO PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL E SEUS NERVOS EM QUATIS (Nasua nasua, LINNAEUS, 1766) Elaine Maria Silva Uberlândia Agosto/2014 Universidade
Universidade Federal de Uberlândia Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária ORIGEM DO PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL E SEUS NERVOS EM QUATIS (Nasua nasua, LINNAEUS, 1766) Elaine Maria Silva Uberlândia Agosto/2014 Universidade
Origin and distribution of the ischiatic nerve in mixed-breed sheep
 102 Origin and distribution of the ischiatic nerve in mixed-breed sheep Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em ovinos sem raça definida Bruno Gomes VASCONCELOS 1 ; Márcia Carolina Domingues SANTOS
102 Origin and distribution of the ischiatic nerve in mixed-breed sheep Origem e distribuição do nervo isquiático em ovinos sem raça definida Bruno Gomes VASCONCELOS 1 ; Márcia Carolina Domingues SANTOS
Segredos da comédia stand-up (Portuguese Edition) By Léo Lins
 Segredos da comédia stand-up (Portuguese Edition) By Léo Lins Segredos da comédia stand-up (Portuguese Edition) By Léo Lins Qualquer um pode escrever uma piada? O que é preciso para se tornar um bom comediante
Segredos da comédia stand-up (Portuguese Edition) By Léo Lins Segredos da comédia stand-up (Portuguese Edition) By Léo Lins Qualquer um pode escrever uma piada? O que é preciso para se tornar um bom comediante
AUSÊNCIA DO TRONCO BRAQUIOCEFÁLICO EM CÃO (Canis familiaris)
 REVISTA CIENTÍFICA ELETRÔNICA DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA - ISSN 1679-7353 PUBLICAÇÃO CI ENTÍFICA DA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA E ZOOTECNIA DE GARÇA/FAMED ANO III, NÚMERO, 07, JUNHO DE 2006. PERIODICIDADE:
REVISTA CIENTÍFICA ELETRÔNICA DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA - ISSN 1679-7353 PUBLICAÇÃO CI ENTÍFICA DA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA E ZOOTECNIA DE GARÇA/FAMED ANO III, NÚMERO, 07, JUNHO DE 2006. PERIODICIDADE:
OSSOS DO MEMBRO INFERIOR
 OSSOS DO MEMBRO INFERIOR ARTICULAÇÕES DO MEMBRO INFERIOR Articulação SacroiIíaca: Ligamento sacrotuberal Lig. sacroespinal Lig. Sacroilíacos post. e ant. Lig. Sacroilíacos interósseos Articulação
OSSOS DO MEMBRO INFERIOR ARTICULAÇÕES DO MEMBRO INFERIOR Articulação SacroiIíaca: Ligamento sacrotuberal Lig. sacroespinal Lig. Sacroilíacos post. e ant. Lig. Sacroilíacos interósseos Articulação
Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET103 Anatomia Veterinária II
 0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET10 Anatomia Veterinária II Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 8 Teóricas Práticas Total Duração em semanas:
0 Programa Analítico de Disciplina VET10 Anatomia Veterinária II Departamento de Veterinária - Centro de Ciências Biológicas e da Saúde Número de créditos: 8 Teóricas Práticas Total Duração em semanas:
ATLAS COLORIDO DE ANATOMIA VETERINáRIA DE EQUINOS (EM PORTUGUESE DO BRASIL) BY STANLEY H. ASHDOWN RAYMOND R. DONE
 Read Online and Download Ebook ATLAS COLORIDO DE ANATOMIA VETERINáRIA DE EQUINOS (EM PORTUGUESE DO BRASIL) BY STANLEY H. ASHDOWN RAYMOND R. DONE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ATLAS COLORIDO DE ANATOMIA VETERINáRIA
Read Online and Download Ebook ATLAS COLORIDO DE ANATOMIA VETERINáRIA DE EQUINOS (EM PORTUGUESE DO BRASIL) BY STANLEY H. ASHDOWN RAYMOND R. DONE DOWNLOAD EBOOK : ATLAS COLORIDO DE ANATOMIA VETERINáRIA
Podemos didaticamente dividir a musculatura dos membros superiores em grupos principais: Músculo Origem Inserção Ação Psoas maior proc.
 MIOLOGIA DO ESQUELETO APENDICULAR MIOLOGIA DO MEMBRO INFERIOR Podemos didaticamente dividir a musculatura dos membros superiores em grupos principais: Iliopsoas MÚSCULOS QUE ACIONAM A COXA Psoas maior
MIOLOGIA DO ESQUELETO APENDICULAR MIOLOGIA DO MEMBRO INFERIOR Podemos didaticamente dividir a musculatura dos membros superiores em grupos principais: Iliopsoas MÚSCULOS QUE ACIONAM A COXA Psoas maior
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA LÁZARO ANTONIO DOS SANTOS. ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL DE JAVALI (Sus scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758)
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA LÁZARO ANTONIO DOS SANTOS ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL DE JAVALI (Sus scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758) UBERLÂNDIA 2016 LÁZARO ANTONIO DOS SANTOS ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA LÁZARO ANTONIO DOS SANTOS ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL DE JAVALI (Sus scrofa LINNAEUS, 1758) UBERLÂNDIA 2016 LÁZARO ANTONIO DOS SANTOS ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO
Comparative anatomical study of the leg s nerves of Cebus (barbed capuchins) with baboons, chimpanzees and modern humans 1
 Comparative anatomical study of the leg s nerves of Cebus (barbed capuchins) with baboons, chimpanzees and modern humans 1 Tainá de Abreu 2, Gabriel A. Pfrimer 2, Roqueline A.G.M.F. Aversi-Ferreira 2,
Comparative anatomical study of the leg s nerves of Cebus (barbed capuchins) with baboons, chimpanzees and modern humans 1 Tainá de Abreu 2, Gabriel A. Pfrimer 2, Roqueline A.G.M.F. Aversi-Ferreira 2,
ROTEIRO DE ESTUDO Membro inferior
 ROTEIRO DE ESTUDO Membro inferior NERVOS Os nervos que inervam o membro inferior originam-se do plexo lombar, situado no abdome, e do plexo sacral, situado na pelve. Plexo Lombar: Plexo Sacral: Nervos
ROTEIRO DE ESTUDO Membro inferior NERVOS Os nervos que inervam o membro inferior originam-se do plexo lombar, situado no abdome, e do plexo sacral, situado na pelve. Plexo Lombar: Plexo Sacral: Nervos
Célia Antunes Barroca. Subsídios do Governo no âmbito do SNC NCRF 22. Universidade de Aveiro Ano 2011
 Universidade de Aveiro Ano 2011 Instituto Superior de Contabilidade e Administração Célia Antunes Barroca Subsídios do Governo no âmbito do SNC NCRF 22 Universidade de Aveiro Ano 2011 Instituto Superior
Universidade de Aveiro Ano 2011 Instituto Superior de Contabilidade e Administração Célia Antunes Barroca Subsídios do Governo no âmbito do SNC NCRF 22 Universidade de Aveiro Ano 2011 Instituto Superior
Músculos do membro inferior. Carlomagno Bahia
 Músculos do membro inferior Carlomagno Bahia Ossos do quadril Superficiais; Região glútea: Profundos. Músculos do membro inferior Coxa: Compartimento anterior; Compartimento medial; Compartimento posterior.
Músculos do membro inferior Carlomagno Bahia Ossos do quadril Superficiais; Região glútea: Profundos. Músculos do membro inferior Coxa: Compartimento anterior; Compartimento medial; Compartimento posterior.
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DA PARAÍBA CENTRO DE CIÊNCIAS AGRÁRIAS CURSO DE BACHARELADO EM MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA
 UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DA PARAÍBA CENTRO DE CIÊNCIAS AGRÁRIAS CURSO DE BACHARELADO EM MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DESCRIÇÃO DE NERVOS DOS PLEXOS LOMBAR E SACRAL EM BICHO- PREGUIÇA-DE-GARGANTA-MARROM (Bradypus variegatus,
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DA PARAÍBA CENTRO DE CIÊNCIAS AGRÁRIAS CURSO DE BACHARELADO EM MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA DESCRIÇÃO DE NERVOS DOS PLEXOS LOMBAR E SACRAL EM BICHO- PREGUIÇA-DE-GARGANTA-MARROM (Bradypus variegatus,
COMPLICAÇÕES NEUROLÓGICAS PÓS-CIRURGIA BARIÁTRICA: UMA REVISÃO DE LITERATURA
 Rev Bras Neurol. 53(3):5-13, 2017 COMPLICAÇÕES NEUROLÓGICAS PÓS-CIRURGIA BARIÁTRICA: UMA REVISÃO DE LITERATURA NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS POST-BARIATRIC SURGERY: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Joana Carvalho
Rev Bras Neurol. 53(3):5-13, 2017 COMPLICAÇÕES NEUROLÓGICAS PÓS-CIRURGIA BARIÁTRICA: UMA REVISÃO DE LITERATURA NEUROLOGICAL COMPLICATIONS POST-BARIATRIC SURGERY: A REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Joana Carvalho
Prova de Seleção Mestrado LINGUA INGLESA 15/02/2016
 Prova de Seleção Mestrado LINGUA INGLESA 15/02/2016 Instruções aos candidatos: (1) Preencher somente o número de inscrição em todas as folhas. (2) Usar caneta preta ou azul. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
Prova de Seleção Mestrado LINGUA INGLESA 15/02/2016 Instruções aos candidatos: (1) Preencher somente o número de inscrição em todas as folhas. (2) Usar caneta preta ou azul. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
MÚSCULOS DO OMBRO. Músculos do Ombro
 MÚSCULOS DO OMBRO Músculos do Ombro Deltóide Supra-espinhal Infra-espinhal Redondo Menor Redondo Maior Subescapular DELTÓIDE Ombro Inserção Proximal: 1/3 lateral da borda anterior da clavícula, acrômio
MÚSCULOS DO OMBRO Músculos do Ombro Deltóide Supra-espinhal Infra-espinhal Redondo Menor Redondo Maior Subescapular DELTÓIDE Ombro Inserção Proximal: 1/3 lateral da borda anterior da clavícula, acrômio
DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DO PLEXO BRAQUIAL DE TATU-CANASTRA (Priodontes maximus Kerr, 1792) - ESTUDO DE CASO
 DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DO PLEXO BRAQUIAL DE TATU-CANASTRA (Priodontes maximus Kerr, 1792) - ESTUDO DE CASO Mayara Marques Pereira Fernandes 1, Susan Christina Braga Domingos 1, Moisés Barbosa de Souza 2,
DESCRIÇÃO ANATÔMICA DO PLEXO BRAQUIAL DE TATU-CANASTRA (Priodontes maximus Kerr, 1792) - ESTUDO DE CASO Mayara Marques Pereira Fernandes 1, Susan Christina Braga Domingos 1, Moisés Barbosa de Souza 2,
Miologia do membro pélvico da paca (Cuniculus paca Linnaeus, 1766) 1
 DOI: 10.1590/S0100-736X2015001300005 Miologia do membro pélvico da paca (Cuniculus paca Linnaeus, 1766) 1 Leonardo M. Leal 2 *, Rafaela M. de Sá 3, Fabricio S. de Oliveira 3, Tais H.C. Sasahara 3, Bruno
DOI: 10.1590/S0100-736X2015001300005 Miologia do membro pélvico da paca (Cuniculus paca Linnaeus, 1766) 1 Leonardo M. Leal 2 *, Rafaela M. de Sá 3, Fabricio S. de Oliveira 3, Tais H.C. Sasahara 3, Bruno
ESTUDO DA ANATOMIA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA DE Cebus libidinosus (MACACO-PREGO) (PRIMATES, CEBIDAE) ASSOCIADO AOS ASPECTOS COMPORTAMENTAIS
 ESTUDO DA ANATOMIA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA DE Cebus libidinosus (MACACO-PREGO) (PRIMATES, CEBIDAE) ASSOCIADO AOS ASPECTOS COMPORTAMENTAIS Sarah de Sousa Garrido 1 ;Tales Alexandre Aversi-Ferreira 2 1 Aluno
ESTUDO DA ANATOMIA DOS MÚSCULOS DA PERNA DE Cebus libidinosus (MACACO-PREGO) (PRIMATES, CEBIDAE) ASSOCIADO AOS ASPECTOS COMPORTAMENTAIS Sarah de Sousa Garrido 1 ;Tales Alexandre Aversi-Ferreira 2 1 Aluno
Guia para Formacao de Analistas de Processos: Gestão Por Processos de Forma Simples (Portuguese Edition)
 Guia para Formacao de Analistas de Processos: Gestão Por Processos de Forma Simples (Portuguese Edition) Mr. Gart Capote Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Guia para Formacao de Analistas
Guia para Formacao de Analistas de Processos: Gestão Por Processos de Forma Simples (Portuguese Edition) Mr. Gart Capote Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Guia para Formacao de Analistas
EFEITO DO TREINAMENTO DE EXERCÍCIOS DE FLEXIBILIDADE SOBRE A MARCHA DE IDOSAS
 FABIANO CRISTOPOLISKI EFEITO DO TREINAMENTO DE EXERCÍCIOS DE FLEXIBILIDADE SOBRE A MARCHA DE IDOSAS Dissertação de Mestrado defendida como pré-requisito para a obtenção do título de Mestre em Educação
FABIANO CRISTOPOLISKI EFEITO DO TREINAMENTO DE EXERCÍCIOS DE FLEXIBILIDADE SOBRE A MARCHA DE IDOSAS Dissertação de Mestrado defendida como pré-requisito para a obtenção do título de Mestre em Educação
Técnicas Adicionais de Estudo dos Nervos (Nervos que Raramente São Estudados)
 Técnicas Adicionais de Estudo dos Nervos (Nervos que Raramente São Estudados) Sergey Nickolaev www.neurosoftbrasil.com.br Estudo do Nervo Cutâneo Lateral do Antebraço Anatomia: O nervo cutâneo do antebraço
Técnicas Adicionais de Estudo dos Nervos (Nervos que Raramente São Estudados) Sergey Nickolaev www.neurosoftbrasil.com.br Estudo do Nervo Cutâneo Lateral do Antebraço Anatomia: O nervo cutâneo do antebraço
Lucas de Assis Soares, Luisa Nunes Ramaldes, Taciana Toledo de Almeida Albuquerque, Neyval Costa Reis Junior. São Paulo, 2013
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELS AND THROUGH THE ANALYSIS OF AIR QUALITY IN THE METROPOLITAN REGION OF GRANDE VITÓRIA Lucas de Assis Soares, Luisa Nunes Ramaldes, Taciana Toledo de
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF THE ATMOSPHERIC DISPERSION MODELS AND THROUGH THE ANALYSIS OF AIR QUALITY IN THE METROPOLITAN REGION OF GRANDE VITÓRIA Lucas de Assis Soares, Luisa Nunes Ramaldes, Taciana Toledo de
Estudo anatômico da porção intrapélvica do nervo isquiático em fetos de bovinos azebuados
 302 Estudo anatômico da porção intrapélvica do nervo isquiático em fetos de bovinos azebuados Rosa Helena dos Santos FERRAZ 1 Gilmar Rodrigues LOPES 1 Alan Peres Ferraz de MELO 1 Irvênia Luiza de Santis
302 Estudo anatômico da porção intrapélvica do nervo isquiático em fetos de bovinos azebuados Rosa Helena dos Santos FERRAZ 1 Gilmar Rodrigues LOPES 1 Alan Peres Ferraz de MELO 1 Irvênia Luiza de Santis
Origem, ramificação e distribuição do nervo radial no braço do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758)
 261 Origem, ramificação e distribuição do nervo radial no braço do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758) Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 1 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 1 André Luiz Quagliatto
261 Origem, ramificação e distribuição do nervo radial no braço do gato doméstico (Felis catus domesticus, Linnaeus 1758) Gregório Corrêa GUIMARÃES 1 Márcia Rita Fernandes MACHADO 1 André Luiz Quagliatto
EXECUTIVE MANUAL OF THE INVESTOR IN THE STATE OF PARÁ
 EXECUTIVE MANUAL OF THE INVESTOR IN THE STATE OF PARÁ Secretaria de Desenvolvimento Econômico, Mineração e Energia EXECUTIVE MANUAL OF THE INVESTOR IN THE STATE OF PARÁ 2 3 The State Government, through
EXECUTIVE MANUAL OF THE INVESTOR IN THE STATE OF PARÁ Secretaria de Desenvolvimento Econômico, Mineração e Energia EXECUTIVE MANUAL OF THE INVESTOR IN THE STATE OF PARÁ 2 3 The State Government, through
UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA
 i UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus LINNAEUS, 1758) DA LINHAGEN PEN AR LAN Lázaro
i UNIVERSIDADE FEDERAL DE UBERLÂNDIA FACULDADE DE MEDICINA VETERINÁRIA ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO ISQUIÁTICO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus LINNAEUS, 1758) DA LINHAGEN PEN AR LAN Lázaro
DIAGNÓSTICO DE MATEMÁTICA
 Não esqueça de se cadastrar no site. Não utilize nenhum rascunho, deixe todas as suas anotações registradas e informe o tempo utilizado na resolução. NOME: TEL: TEMPO UTILIZADO NA RESOLUÇÃO: 1. Macey is
Não esqueça de se cadastrar no site. Não utilize nenhum rascunho, deixe todas as suas anotações registradas e informe o tempo utilizado na resolução. NOME: TEL: TEMPO UTILIZADO NA RESOLUÇÃO: 1. Macey is
GERENCIAMENTO PELAS DIRETRIZES (PORTUGUESE EDITION) BY VICENTE FALCONI
 Read Online and Download Ebook GERENCIAMENTO PELAS DIRETRIZES (PORTUGUESE EDITION) BY VICENTE FALCONI DOWNLOAD EBOOK : GERENCIAMENTO PELAS DIRETRIZES (PORTUGUESE Click link bellow and free register to
Read Online and Download Ebook GERENCIAMENTO PELAS DIRETRIZES (PORTUGUESE EDITION) BY VICENTE FALCONI DOWNLOAD EBOOK : GERENCIAMENTO PELAS DIRETRIZES (PORTUGUESE Click link bellow and free register to
Service quality in restaurants: an experimental analysis performed in Brazil
 . XIII INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Energy that moves production: a dialogue among integration, project and sustainability 09-11 October 2007 Service quality
. XIII INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING AND OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT Energy that moves production: a dialogue among integration, project and sustainability 09-11 October 2007 Service quality
Implementation of BE requirements: Brazilian Experience
 13 th ICDRA Implementation of BE requirements: Brazilian Experience RODRIGO CRISTOFOLETTI Head of Department of Bioequivalence Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) Historical view Future
13 th ICDRA Implementation of BE requirements: Brazilian Experience RODRIGO CRISTOFOLETTI Head of Department of Bioequivalence Brazilian National Health Surveillance Agency (ANVISA) Historical view Future
UNIVERSIDADE CATÓLICA PORTUGUESA. Dissertação apresentada à Universidade Católica Portuguesa para obtenção do grau de Mestre em Ensino de Música
 UNIVERSIDADE CATÓLICA PORTUGUESA O ARCO CONTRIBUTOS DIDÁTICOS AO ENSINO DO VIOLINO Dissertação apresentada à Universidade Católica Portuguesa para obtenção do grau de Mestre em Ensino de Música Ana Catarina
UNIVERSIDADE CATÓLICA PORTUGUESA O ARCO CONTRIBUTOS DIDÁTICOS AO ENSINO DO VIOLINO Dissertação apresentada à Universidade Católica Portuguesa para obtenção do grau de Mestre em Ensino de Música Ana Catarina
Origem e distribuição do nervo axilar em tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla)
 Biotemas, 25 (3), 249-255, setembro de 2012 ISSNe 2175-7925 249 doi: 10.5007/2175-7925.2012v25n3p249 Origem e distribuição do nervo axilar em tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Luciana Aparecida
Biotemas, 25 (3), 249-255, setembro de 2012 ISSNe 2175-7925 249 doi: 10.5007/2175-7925.2012v25n3p249 Origem e distribuição do nervo axilar em tamanduá-bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla) Luciana Aparecida
ARTÉRIAS DOS LOBOS CERVICAIS DO TIMO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS DA RAÇA PIAU
 ARS VETERINARIA, Jaboticabal, ISSN 0102-6380 ARTÉRIAS DOS LOBOS CERVICAIS DO TIMO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS DA RAÇA PIAU (ARTERIES OF THE CERVICAL LOBES OF THE THYMUS IN SWINE FETUS OF THE PIAU BREED) F. O. C.
ARS VETERINARIA, Jaboticabal, ISSN 0102-6380 ARTÉRIAS DOS LOBOS CERVICAIS DO TIMO EM FETOS DE SUÍNOS DA RAÇA PIAU (ARTERIES OF THE CERVICAL LOBES OF THE THYMUS IN SWINE FETUS OF THE PIAU BREED) F. O. C.
Um olhar que cura: Terapia das doenças espirituais (Portuguese Edition)
 Um olhar que cura: Terapia das doenças espirituais (Portuguese Edition) Padre Paulo Ricardo Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Um olhar que cura: Terapia das doenças espirituais (Portuguese
Um olhar que cura: Terapia das doenças espirituais (Portuguese Edition) Padre Paulo Ricardo Click here if your download doesn"t start automatically Um olhar que cura: Terapia das doenças espirituais (Portuguese
MEMBROS INFERIORES. Anatomia Humana Segmentar Profª. Kátia Nóbrega Profª. Terezinha Nóbrega
 MEMBROS INFERIORES Anatomia Humana Segmentar Profª. Kátia Nóbrega Profª. Terezinha Nóbrega INTRODUÇÃO A Anatomia Segmentar divide o corpo humano em diferentes segmentos para melhor analisá-los. Considerando
MEMBROS INFERIORES Anatomia Humana Segmentar Profª. Kátia Nóbrega Profª. Terezinha Nóbrega INTRODUÇÃO A Anatomia Segmentar divide o corpo humano em diferentes segmentos para melhor analisá-los. Considerando
LUMBOSACRAL PLEXUS OF THE MONGOLIAN GERBIL (Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867)
 Original Article 713 LUMBOSACRAL PLEXUS OF THE MONGOLIAN GERBIL (Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867) PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL DO GERBIL (Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867) Hélio Noberto de ARAÚJO
Original Article 713 LUMBOSACRAL PLEXUS OF THE MONGOLIAN GERBIL (Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867) PLEXO LOMBOSSACRAL DO GERBIL (Meriones unguiculatus Milne-Edwards, 1867) Hélio Noberto de ARAÚJO
MATERIAL E MÉTODOS Utilizaram-se 30 fetos de suínos da raça Hampshire, sendo 10 fêmeas e 20 machos, doados após abortos espontâneos de fêmeas gestante
 Original Article IRRIGAÇÃO DAS GLÂNDULAS ADRENAIS EM SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus - Linnaeus, 1758) DA RAÇA HAMPSHIRE IRRIGATION OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS IN HAMPSHIRE SWINE (Sus scrofa domesticus - Linnaeus,
Original Article IRRIGAÇÃO DAS GLÂNDULAS ADRENAIS EM SUÍNOS (Sus scrofa domesticus - Linnaeus, 1758) DA RAÇA HAMPSHIRE IRRIGATION OF THE ADRENAL GLANDS IN HAMPSHIRE SWINE (Sus scrofa domesticus - Linnaeus,
FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO THIAGO BRANDÃO DA CUNHA
 FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO THIAGO BRANDÃO DA CUNHA THE INTEGRATION PROCESS AFTER INTERNATIONAL ACQUISITION OF A COMPANY INSIDE THE CACHAÇA SECTOR IN BRAZIL: A CASE STUDY RIO DE JANEIRO 2018 THIAGO
FEDERAL UNIVERSITY OF RIO DE JANEIRO THIAGO BRANDÃO DA CUNHA THE INTEGRATION PROCESS AFTER INTERNATIONAL ACQUISITION OF A COMPANY INSIDE THE CACHAÇA SECTOR IN BRAZIL: A CASE STUDY RIO DE JANEIRO 2018 THIAGO
Toxoplasma gondii em Tamanduá Bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus 1758) da região Noroeste do Estado de São Paulo
 Toxoplasma gondii em Tamanduá Bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus 758) da região Noroeste do Estado de São Paulo LUIZ PAULO NOGUEIRA AIRES, VINICIUS MATHEUS FERRARI 2, HERBERT SOUSA SOARES, CINARA
Toxoplasma gondii em Tamanduá Bandeira (Myrmecophaga tridactyla, Linnaeus 758) da região Noroeste do Estado de São Paulo LUIZ PAULO NOGUEIRA AIRES, VINICIUS MATHEUS FERRARI 2, HERBERT SOUSA SOARES, CINARA
ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO AXILAR EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE AXILLARY NERVE IN ZEBU-CROSSED BOVINE FETUSES
 Original Article 946 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO AXILAR EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE AXILLARY NERVE IN ZEBU-CROSSED BOVINE FETUSES Frederico Balbino LIZARDO 1 ; Frederico
Original Article 946 ORIGEM E DISTRIBUIÇÃO DO NERVO AXILAR EM FETOS DE BOVINOS AZEBUADOS ORIGIN AND DISTRIBUTION OF THE AXILLARY NERVE IN ZEBU-CROSSED BOVINE FETUSES Frederico Balbino LIZARDO 1 ; Frederico
Formação do plexo braquial e sistematização dos territórios nervosos em membros torácicos de lobosmarinhos Arctocephalus australis
 168 Formação do plexo braquial e sistematização dos territórios nervosos em membros torácicos de lobosmarinhos Arctocephalus australis Brachial plexus formation and the nervous territories on thoracic
168 Formação do plexo braquial e sistematização dos territórios nervosos em membros torácicos de lobosmarinhos Arctocephalus australis Brachial plexus formation and the nervous territories on thoracic
Faculdade de Medicina Veterinária (Laboratório de Pesquisas em Animais Silvestres) da Universidade Federal de Uberlândia; 2
 Archives of Veterinary Science v. 9, n. 2, p. 67-72, 2004 Printed in Brazil ISSN: 1517-784X TOPOGRAFIA DOS COLATERAIS CALIBROSOS DO ARCO AÓRTICO DE UM MÃO - PELADA (Procyon cancrivorus GRAY, 1865) (CARNIVORA
Archives of Veterinary Science v. 9, n. 2, p. 67-72, 2004 Printed in Brazil ISSN: 1517-784X TOPOGRAFIA DOS COLATERAIS CALIBROSOS DO ARCO AÓRTICO DE UM MÃO - PELADA (Procyon cancrivorus GRAY, 1865) (CARNIVORA
ESTUDO ANATÓMICO DA INERVAÇÃO DA PORÇÃO DISTAL DO MEMBRO TORÁCICO EM EQÜINO
 Ciência Rural, Santa Maria, v.27, n.1, p.67-73, 1997 ISSN 0103-8478 67 ESTUDO ANATÓMICO DA INERVAÇÃO DA PORÇÃO DISTAL DO MEMBRO TORÁCICO EM EQÜINO ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE INERVATION OF THE DISTAL PORTION
Ciência Rural, Santa Maria, v.27, n.1, p.67-73, 1997 ISSN 0103-8478 67 ESTUDO ANATÓMICO DA INERVAÇÃO DA PORÇÃO DISTAL DO MEMBRO TORÁCICO EM EQÜINO ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE INERVATION OF THE DISTAL PORTION
FCL Capital March 2019
 Performance FCL Hedge First Quarter 2019 6,48% First Quarter 2019 % CDI 428,76% Since Inception 13,16% Annualized since inception 5,86% FCL Opportunities First quarter 2019 in BRL 24,63% First quarter
Performance FCL Hedge First Quarter 2019 6,48% First Quarter 2019 % CDI 428,76% Since Inception 13,16% Annualized since inception 5,86% FCL Opportunities First quarter 2019 in BRL 24,63% First quarter
NORMAS DE FUNCIONAMENTO DOS CURSOS DE LÍNGUAS (TURMAS REGULARES E INTENSIVAS) 2015/2016
 NORMAS DE FUNCIONAMENTO DOS CURSOS DE LÍNGUAS (TURMAS REGULARES E INTENSIVAS) 2015/2016 1. Tipos de turma e duração: O CLECS oferece dois tipos de turma: regular e intensivo. Além destas turmas, o CLECS
NORMAS DE FUNCIONAMENTO DOS CURSOS DE LÍNGUAS (TURMAS REGULARES E INTENSIVAS) 2015/2016 1. Tipos de turma e duração: O CLECS oferece dois tipos de turma: regular e intensivo. Além destas turmas, o CLECS
ARTÉRIAS E SEGMENTOS ANATOMOCIRÚRGICOS DA GLÂNDULA ADRENAL EM FETOS DE BOVINOS
 Braz. J. vet. Res. anim. Sci., São Paulo, v. 32, n.2, p. 75-82, 1995. ARTÉRIAS E SEGMENTOS ANATOMOCIRÚRGICOS DA GLÂNDULA ADRENAL EM FETOS DE BOVINOS ARTERIES AND ANA TOMICOSURGICAL SEGMENTS OF THE ADRENAL
Braz. J. vet. Res. anim. Sci., São Paulo, v. 32, n.2, p. 75-82, 1995. ARTÉRIAS E SEGMENTOS ANATOMOCIRÚRGICOS DA GLÂNDULA ADRENAL EM FETOS DE BOVINOS ARTERIES AND ANA TOMICOSURGICAL SEGMENTS OF THE ADRENAL
Sistematização dos territórios nervosos do plexo braquial em chinchila (Chinchilla lanigera)
 283 Sistematização dos territórios nervosos do plexo braquial em chinchila (Chinchilla lanigera) Conrado de Oliveira GAMBA 1 Tiane Ferreira de CASTRO 1 Eduardo Madruga RICKES 2 Malcon Andrei Martinez PEREIRA
283 Sistematização dos territórios nervosos do plexo braquial em chinchila (Chinchilla lanigera) Conrado de Oliveira GAMBA 1 Tiane Ferreira de CASTRO 1 Eduardo Madruga RICKES 2 Malcon Andrei Martinez PEREIRA
